基金项目:云南省地震科技创新团队(CXTD202401); 国家自然科学基金面上项目(52278489); 河北省高等学校科学研究项目(BJK2022066).
第一作者简介:阿拉塔(1978-),高级工程师,博士,主要从事建筑结构抗震研究.E-mail:alata182@126.com.
(1.云南省地震局,云南 昆明 650224; 2.防灾科技学院,河北 三河 065201; 3.中国地震局工程力学研究所,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150080; 4.中国地震局地球物理研究所,北京 100081; 5.嘉应学院 土木工程学院,广东 梅州 514015)
(1.Yunnan Earthquake Agency,Kunming 650024,Yunnan,China)(2.Institute of Disaster Prevention,Sanhe 065201,Hebei,China)(3.Institute of Engineering Mechanics,China Earthquake Administration,Harbin 150080,Heilongjiang,China)(4.Institute of Geophysics,China Earthquake Administration,Beijing 100081,China)(5.School of Civil Engineering,Jiaying University,Meizhou 514015,Guangdong,China)
earthquake damage investigation; collapse mechanism; hard brittle component; weakly extended component; deformation saturation; collapse trigger point
DOI: 10.20015/j.cnki.ISSN1000-0666.2024.0053
地震灾区房屋建筑的破坏、倒塌是造成人员伤亡的最主要原因。调查建筑结构地震灾害,总结经验教训,对提高建筑结构抗震性能和推动地震工程学科发展具有重要意义。建筑结构地震倒塌机理一直是结构抗震研究的核心课题(顾祥林等,2015; 郭迅,2018)。
从2008年四川汶川8.0级地震至2022年四川泸定6.8级地震的14年间,在我国西南地区发生了十余次强地震,造成了大量的建筑结构破坏、倒塌,不同结构体系的房屋在地震中呈现出的破坏模式也不尽相同。地震灾区震害调查发现,有大量的、经过抗震设计的建筑结构也发生了破坏甚至倒塌,且一些震害现象也有所重复。例如,框架结构震害显著,且底层框架砌体混合结构倒塌比例高(公茂盛等,2013; 杨永强等,2014; 王多智等,2018; 张令心等,2019; 李昆等,2021; 罗若帆等,2022; 谢贤鑫,2022; 雷雅婷等,2022)。现场震害调查还发现,发生破坏及倒塌的建筑结构存在“散”“脆”“偏”“单”等缺陷,其中,“偏”的缺陷最为普遍,但一直未引起研究人员的重视。
多层建筑结构是目前我国城乡建设中的主要建筑类型。对于高度不超过40 m,以剪切变形为主且质量、刚度沿竖向分布较为均匀的结构,我国《建筑抗震设计规范》(GB 50011—2010)推荐采用底部剪力法进行计算。另外,由于重力和地震剪力由上往下逐层累加,结构底层的地震剪力和竖向荷载最大,震害调查结果也显示底层震害最重。因此本文主要分析近14年来我国地震灾区建筑底层的结构平面布局、构造差异及抗侧力构件特征,对比分析“坏”与“不坏”建筑的差异,根据现场调查得到的多层建筑震害,分析震害原因,寻找建筑结构抗震缺陷,探究建筑结构地震倒塌机理。
自2008年四川汶川8.0级地震以来,我国地震工作者对历年发生的破坏性地震现场震害作了细致的调查,对各类建筑结构震害特点进行了深入分析,认为在破坏性地震中建筑结构发生破坏及倒塌是由于其自身存在 “散”“脆”“偏”“单”等抗震缺陷所致,下面对这些缺陷引起的震害进行讨论。
房屋建筑中“散”的缺陷主要体现为结构的水平构件与竖向构件的连接不满足要求或未进行有效连接,整体性差。我国农村地区自建的土木结构、砖木结构的震害如图1所示。由图1a可见,木构架与土墙无有效连接措施,且外围各方向墙体间连接差,墙体直接由土坯砌筑,未采取加强措施; 由图1b可见,支撑屋面的檩条及椽子直接搭设在土墙上,在地震动的惯性作用下墙体开裂、外闪,导致墙倒屋塌。由图1c、d可见,砖木结构中外围纵横墙间无有效连接或连接薄弱,砖墙与木构架之间无连接措施,整体性差。一般外围砖墙无加强措施,砌筑过程中既无水平系梁也未设置构造柱,整体抗侧刚度小。另外,瓦片与屋面间无固定措施,只是将瓦片压边叠放,易发生梭瓦破坏,砌体结构中无完善的圈梁、构造柱抗震措施。纵横墙间无构造柱或连接薄弱,门窗洞口两侧无构造柱,楼板与梁连接不满足要求,如图2a~c所示。框架结构中女儿墙的预埋件未采取加强措施,填充墙与主体结构间拉结措施缺失或拉结筋不满足要求,导致地震作用下发生破坏,如图2d、e所示。另外,山墙高度和宽度超过规范限值,却未采取规定的加强措施,导致剪切破坏,如图2f所示。
图1 鲁甸MS6.5地震中土木结构和砖木结构震害
Fig.1 Seismic damage of civil structures and brick wood structures in the Ludian MS6.5 earthquake
房屋建筑因“脆”的缺陷引起的破坏甚至倒塌可以从以下两个方面分析;
首先,建筑结构材料方面,土木结构的墙体采用红泥土夯堆而起,未添加任何加筋材料; 墙体下宽上窄呈梯形,无加固措施,脆性十足,如图3a所示。砖木结构中用砖砌块将木构架柱裹砌的砖柱,在横向椽子支撑点处应力集中形成贯通的竖向裂缝,如图3b所示。砌体结构中砖柱、砖墙在地震动作用下发生脆性剪切破坏,如图3c所示。
其次,房屋建筑中因洞口的设置使墙体分割成若干段墙肢。在抗震设计中,墙体按照高宽比不同计算其抗侧刚度,当高宽比小于1时只考虑剪切变形(卢存恕,1999),即地震中剪切作用为主导,形成斜裂缝或交叉裂缝,如图3d所示。框架结构中由于墙体的布设使框架柱计算高度变小,产生短柱效应,在地震中易发生脆性剪切破坏,如图3e所示。常见的震害现象如图3f所示,由于门窗洞口的设置形成矮墙,其变形能力差,类似“短柱”效应,易发生脆性剪切破坏。
由于墙体的布设使建筑平面内纵向各轴抗侧刚度差异巨大,地震动作用下地震剪力按照关键构件的抗侧刚度分配,地震剪力率先在刚度大、延性差的构件上集中发生破坏,而此时刚度小、延性好的构件分配的地震剪力较小,尚未发挥作用处于完好状态(郭迅,2018; 王波,2020; 郭富强,2023),这就是房屋建筑中“偏”的缺陷引起建筑结构的破坏。在破坏性震中由“偏”的缺陷引起结构破坏甚至倒塌的现象比比皆是,如图4所示。我国西南乡镇地区,框架砌体混合结构大量存在,以图4a为例,该建筑一层平面内纵向三道轴线,临街一侧轴线因使用需求大,开门洞无墙体,进深向第二、第三轴线布设墙体,在地震动作用下临街一侧的框架柱完好,而第二道轴线的墙体发生严重破坏。图4b中建筑一层纵向第一、第二轴线纵向为无墙框架柱,地震中完好,进深第三轴为带构造柱的墙体,破坏严重。
图4 汶川地震(a)和泸定地震中(b)框架砌体混合结构一层震害
Fig.4 Seismic damage to the first floor of the frame masonry mixed structure in the Wenchuan earthquake(a)and the Luding earthquake(b)
建筑抗震概念设计要求建筑结构布局均匀规整,体形力求简单,选择抗震有利的平立面,抗侧力构件的刚度、强度和质量分布在空间上均衡且连续,避免薄弱层(部位),产生应力和变形集中。图5为汶川8.0级地震灾区建筑结构由沿高度方向存在“偏”的缺陷而发生破坏的情况。图5a为一栋钢筋混凝土框架结构,建筑一层为空旷框架柱,整栋建筑刚度、强度质量在竖向不连续底部产生薄弱层; 图5b所示建筑一层为框架,二层以上为砌体结构,竖向结构体系发生变化造成薄弱层,二层发生垮塌破坏。建筑结构竖向不规则,在地震中容易发生“层屈服”的破坏模式。
图5 汶川8.0级地震灾区建筑结构层破坏
Fig.5 The layer destruction of the buildings in the Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake
房屋建筑中“单”的缺陷主要由建筑抗震设防体系单一、各构件协同工作能力差、结构赘余度不足造成。地震发生时,建筑物的某个关键构件发生破坏后承载力迅速降低,可能形成机构失稳而连续倒塌破坏,如图6a所示。砌体结构中缺失完善的圈梁构造柱抗震构造措施,也是结构“单”的表现。单跨多层框架结构广泛应用于中小学教学楼、厂房; 一层只有框架柱作为抗侧力和承重的关键构件,冗余度不足,也是结构“单”的缺陷,如图6b所示。
房屋建筑作为基础、墙、梁、板及柱等构件的集合体,在地震中各构件间互相联系,共同抵御地震作用。地震中建筑结构破坏甚至倒塌是由个别构件或局部构件先破坏引起的,建筑结构存在的“散”“脆”“偏”“单” 等抗震缺陷,在结构破坏中有可能是其中一个或多个缺陷导致的。例如,土木结构、砖木结构在地震中发生破坏、倒塌就是由结构的“散”“脆”的缺陷导致的,如图1、2f、3a所示; 砌体结构中砂浆强度不达标、圈梁构造柱不完善及砖柱未进行加强措施等造成的破坏是结构的“散”“脆”缺陷的综合体现,如图3c、d所示; 框架结构中由填充墙的布置引起的面内刚度不均衡和框架柱的短柱效应是结构的“偏”“脆”缺陷的体现,如图3e、f和图4所示; 另外,砌体结构中缺失完善的圈梁构造柱抗震构造措施,不仅是“散”的缺陷,也是“单”的表现。
图6 汶川8.0级地震中建筑结构“单”的缺陷
Fig.6 The defect of the “lack of redundancy” of buildings in the Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake
多层钢筋混凝土框架结构和框架砌体混合结构在历次地震中的破坏、倒塌比例较高,尤其是框架砌体混合结构。混凝土因其强度高、可塑性强、耐久性好成为建筑工程主要材料。框架结构因其空间布置灵活、自重轻、传力途径明确等特点成为公共建筑的首选结构体系。另外,城镇地区街道两侧多层建筑以一层为商用框架结构、二层以上为民居的砌体结构为主的框架砌体混合结构居多。上节就建筑结构抗震缺陷进行了分析,但“偏”的缺陷较其他缺陷更普遍,未得到重视。本节基于实际震害进一步对“偏”的缺陷进行分析探讨。笔者以这两种结构体系为研究对象,揭示建筑结构“偏”的缺陷,解释震害现象,探究其破坏原因。
长宁县双河中学位于2019年四川长宁6.0级地震极震区。双河中学教学楼为四层钢筋混凝土框架结构,每层的柱网布局相同,层高均为3.6 m,建筑总高度为15.1 m,建筑总面积约2 400 m2; 当地抗震设防烈度为Ⅶ度,设计基本地震加速度值0.1 g。该教学楼纵向三轴10跨,横向十一轴2跨,教学楼正面、背面及一层平面图如图7所示。
图7 双河中学教学楼正面(a)、背面(b)和一层平面图(c)
Fig.7 The front(a),back(b)and plan of the 1st floor(c)of a teaching building in Shuanghe middle school
由图7c可知,纵向仅有3道轴线,其主要差异在于有无填充墙、洞口大小及墙体对框架柱的约束情况; 轴线为无墙的框架柱; 轴线设有高窗和门洞,框架柱约束主要来自窗下墙(墙体较高); 轴线只有窗洞,窗下填充墙和窗间墙限制框架柱的变形。横向有8道满砌填充墙将一层分成若干房间。结构四层平面布局相同,以剪切变形为主,且质量、刚度沿竖向分布均匀; 结构抗震计算可采用底部剪力法进行简化计算,由于结构底层所受的地震剪力最大,这里重点展示教学楼一层的震害。
正是这样的平面布局造成建筑一层纵向各轴线抗侧刚度迥然不同。由图8a可见,双河中学教学楼一层的轴线为无墙的框架柱,地震作用下,框架柱全高度参与变形,抗侧刚度小,延性好,无损伤。
由图8b、c可见,轴线因洞口的布设使墙体分割成若干段,采用高窗户且窗高度小,使窗下填充墙高度高,约束了框架柱变形,在地震作用下框架柱仅窗高部分参与变形,抗侧刚度大,延性差。另外,窗下墙、门头墙高宽比都较小,易发生剪切变形。
图8 双河中学教学楼一层各轴线震害
Fig.8 Seismic damage on the axes of the first floor of the school building in Shuanghe middle school
由图8d、e可见,轴线仅存在窗洞,且窗洞高度较高,使轴框架柱参与变形的高度比轴框架柱参与变形的高度还要高; 轴抗侧刚度比轴抗侧刚度大,但比轴抗侧刚度小; 再者,框架柱窗高部分与两侧墙体共同受力、变形,延性介于轴与轴之间,震害主要出现在窗下墙和窗间墙,破坏程度较轻。
从以上分析可知,建筑纵向因填充墙的布设、洞口的设置造成各轴抗侧刚度、延性差异巨大,平面内刚度不均匀,导致建筑出现“偏”的缺陷。在地震作用下,地震剪力在刚度大的构件上内力集中,率先发生破坏。另外,建筑横向存在多道满砌横墙,面内刚度大,限制了建筑在地震中横向变形,使建筑以纵向平动为主,横墙震害如图8f所示。建筑结构横向均匀布设满砌填充墙,各轴刚度相近,承载能力高,而纵向只有3道轴线,且各轴刚度差异大,承载能力弱,使得纵向成为建筑的抗震薄弱向; 这种纵、横向的刚度、承载能力差异较大的情况,也是“偏”的一种体现。
磨西镇大杉树村6组56号建筑位于2022年四川泸定6.8级地震的极震区,其烈度为Ⅸ度。该建筑共3层,一层为框架砌体混合结构,二、三层为砌体结构。一层轴、轴无墙体,框架柱作为抗侧力和承重构件,轴为带构造柱的承重墙。建筑正面、一层3D示意如图9所示。
图9 大杉树村6组56号建筑正面(a)和一层3D示意图(b)
Fig.9 The front view(a)of No.56 building in Group 6 of Dashanshu Village and 3D schematic diagram(b)of the building's first floor
现场调查发现,一层破坏严重,一层整体纵向侧移近100 mm,二层、三层砌体结构完好,无震害。一层轴框架柱全部震损,柱端出现塑性铰,部分柱端纵向钢筋断裂如图 10a~e所示; 一层轴部分框架柱上端混凝土掉落,钢筋屈服,出塑性铰; 内横墙和山墙发生面外破坏、倒塌,如图 10f~h所示; 一层轴为带构造柱的承重墙,破坏严重,墙体裂缝内外贯通,上部结构下坠,基本丧失承重能力,在地震作用下建筑一层发生扭转破坏,如图 10i~k所示。
图 10 大杉树村6组56号建筑一层震害图
Fig.10 Seismic damage to the first floor of No.56 building in Group 6 of Dashanshu Village
由图9b可知,建筑纵向3道轴线中,轴、轴仅有框架柱,无墙体; 轴为带构造柱的砌体墙,墙体上开设门窗洞口。首先,这种布局使得结构一层抗侧刚度平面内不均衡; 轴、轴抗侧刚度远小于轴抗侧刚度,在地震作用下地震剪力在轴高倍集中,带构造柱的承重墙率先发生剪切破坏,丧失承重能力,上部结构下沉。其次,一层横向墙体少,且偏一侧布置,伴有扭转破坏。这种由平面内刚度不均衡导致的破坏是建筑“偏”缺陷的体现。最后,建筑一层为框架砌体混合结构,抗侧力构件少,二层、三层为砌体结构,墙体布置均匀。竖向墙体不对齐、不连续,造成竖向刚度、强度、质量差异大,造成底层为薄弱层,是建筑“偏”的缺陷的另一种体现。
20世纪70年代,基于实际震害,有学者提出钢筋混凝土框架结构在地震中发生破坏是由于框架柱端出现塑性铰,形成层屈服的破坏机制(Paulay,1981; Paulay,Priestly,1992; Park,1999),即“弱柱强梁”破坏模式。为防止结构出现层屈服破坏,新西兰学者Paulay和Park提出了钢筋混凝土框架结构抗地震倒塌的“能力设计方法”(Capacity Design),强调在地震作用下,框架梁先于框架柱出现塑性铰,通过梁端塑性铰使整个结构有大的内力重分布,让尽可能多的结构构件参与到整体抗震当中,耗散地震能量达到抗震要求。
从2008年汶川8.0级地震至2022年泸定6.8级地震的14年间,多次破坏性地震造成的震害表明,绝大部分钢筋混凝土框架结构破坏发生在柱端,梁构件并未发生破坏,结构工程界期望的“强柱弱梁”的整体破坏模式未出现(清华大学土木结构组等,2008; 叶列平等,2008; 李碧雄等,2009; 温增平等,2019; 郭迅,2019; Günay,Mosalam,2010; 谭皓等,2012; 岳茂光等,2012; 闫培雷等,2014; 李碧雄,2015; Dizhur et al,2016; Bal,Smyrou,2016; Barbosa et al,2017; Yépez et al,2016; Varum et al,2017; 薄景山等,2018; Moya et al,2018; 张令心等,2019; 李昆等,2021; 赵仕兴等,2023)。
钢筋混凝土框架结构“强柱弱梁”的抗震设计在地震中并未发挥作用,实际工程中的很多因素尚未在《建筑抗震设计规范》(GB 50011—2010)所给出的公式6.2.2-1中得到充分体现。叶列平(2008)结合震害调查资料,从填充墙等非结构构件的影响、楼板对框架梁的影响、梁端配筋率和钢筋强度的影响、框架柱轴压比的限值及最小配筋率、配箍率影响等方面分析了“强柱弱梁”屈服机制在建筑结构的实际抗震中未能实现的原因。
汶川8.0级地震后,国内外学者汲取建筑结构现场震害经验教训,提出如下建议:应考虑墙体不同布置方式对结构抗震性能及墙对柱约束影响(郭子雄等,2010; 曹家乐等,2022); 考虑楼板对结构的影响及对框架梁的加强作用(顾祥林,2012); 应考虑墙框连接方式的影响(蒋欢军等,2014); 应减小框架柱轴压比限值(黄思凝,2016); 应提高框架柱端弯矩增大系数(张浩,2019); 应考虑填充墙对框架结构的影响(Teguh,2017; Baghi et al,2018); 应考虑箍筋加密对承载力和变形能力的改变(张炳辉等,2019); 应考虑框架柱剪跨比对结构破坏模式的影响(范晓庆等,2019)。
通过结构抗震实践可知,上述建议效果不理想,且“强柱弱梁”整体屈服机制未能对建筑结构震害现象给出合理的解释。因此,“强柱弱梁”整体屈服机制有可能是存在不足,该机制未能实现的原因有:首先,不能将结构同层的抗侧力和承重构件同等看待,真实建筑结构是不同力学性能的抗侧力构件和竖向承重构件同层并存,共同抵抗地震作用; 其次,建筑中填充墙一般直接砌筑在框架梁上,而梁上墙体对其的约束作用使梁端难以出现塑性变形,出现“弱梁不弱”的情况; 最后,目前抗震理论采用结构承载力和延性的组合抵御设定的地震作用,在罕遇地震作用下,通过结构的塑性变形耗能来弥补结构承载力不足,这要求结构变形需经历弹性阶段、强化阶段、塑性变形阶段和失效阶段; 而在地震动往复作用下,结构从开裂到临界倒塌时的变形很小,无法经历强化阶段和塑性变形阶段就发生破坏倒塌(郭迅,2022)。
每次破坏性地震发生后,都有大量的多层建筑破坏甚至倒塌,而“强柱弱梁”理论对结构的破坏和倒塌未能给出科学的解释。针对这个问题,笔者所在的课题组对地震灾区具有代表性的房屋建筑的震害作了现场调查,经过理论分析、试验研究,提出了基于实际震害的“变形饱和”倒塌机理。
基于实际震害,以映秀镇漩口中学教学楼为原型进行了振动台倒塌试验,通过试验研究发现(王波,2020),受填充墙约束的框架柱端应变为无墙框架柱端应变的4倍左右,且率先发生破坏,即地震剪力在有填充墙框架柱上高倍集中,如图 11a所示的A2柱; 由于满砌横墙的刚度影响,即便结构的刚度中心与质量中心不重合,在地震作用下结构主要沿纵向发生平动,未发生扭转破坏。为了进一步探究墙体对框架柱力学性能的影响,开展了拟静力试验,研究了受墙体约束框架柱和不受墙体约束框架的本构关系,并定义了硬脆构件和弱延构件(A Lata,2022)。
从图 11b所示的各框架柱承载力-位移曲线可知,轴框架柱的本构关系曲线呈现高、陡、窄特征,表明该构件承载力高、刚度大、延性差,称为硬脆构件; 而轴、轴线框架柱的本构关系曲线呈现低、缓、宽特征,表明该构件承载力低、刚度小、延性好,称为弱延构件。地震剪力按照各轴抗侧刚度比例进行分配,即使侧移很小时结构内力就在轴高倍集中,率先发生破坏并触发结构倒塌; 而此时轴、轴线竖向构件承载力和变形能力还远未达到最大值,由轴柱的破坏、承重失效,被连带破坏。
真实建筑结构同层是硬脆构件和弱延构件并存,在地震作用下硬脆构件上内力高倍集中,结构在较小位移下,硬脆构件率先发生脆性破坏并触发结构倒塌。其中,硬脆构件在地震作用下结构内力集中,在较小变形下其承载能力达到极限发生脆性破坏的状态称为变形饱和状态。
得妥镇南头村1组7号建筑位于2022年泸定6.8级地震的Ⅸ度区,为五层,一层破坏严重,二至四层基本完好。现场调查发现,建筑一层为框架砌体混合结构,上部各层为砌体结构。整栋建筑正立面和一层3D示意如图 12a、b所示。
图 11 各框架柱破坏状态(a)和承载力-位移曲线(b)
Fig.11 The failure state of 3 frame columns(a)and the columns' force-displacement curves(b)
建筑一层为商用,临街一侧轴和轴无墙,只有框架柱; 轴和轴设有窗洞带构造柱的承重墙,轴和轴无墙框架柱为抗侧弱延构件,轴和轴带构造柱的承重墙为抗侧硬脆构件。
地震作用下,建筑一层纵向轴、轴无墙体约束框架柱全高度参与变形; 轴、轴带构造柱的承重墙,由于窗洞的设置,将承重墙分为若干墙段共同抵御地震作用。地震剪力在轴、轴墙体高倍集中,承载力达到极限值,承担的内力是其余轴线的约6倍(图 12e、f),同时,变形达到饱和状态发生剪切破坏,窗间墙发生交叉斜裂缝贯通内外,如图 12d所示; 同层的轴、轴框架柱只是柱端混凝土脱落,无其他震害。从图 12c可知,建筑同层由硬脆特性显著的墙体和弱延特性显著的框架柱组成,震害对比鲜明。
在水平地震作用下,总刚度大的轴、轴与总刚度小的轴、轴力-变形曲线如图 12e、f所示,其中,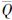 为各轴线上构件抗力比:
为各轴线上构件抗力比:

式中:Q为各轴线上构件承担的水平剪力; fv为构件的抗剪强度; A为构件横截面面积。
图中θ为层间位移角:
θ=δ/h (2)
式中:δ为楼板侧向位移; h为底层净高。
由图 12e可见,轴、轴的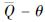 曲线又陡又高,容易快速达到饱和(图中S点)而丧失承重能力,后因重力压垮导致结构倒塌。由图 12f可见,轴、轴
曲线又陡又高,容易快速达到饱和(图中S点)而丧失承重能力,后因重力压垮导致结构倒塌。由图 12f可见,轴、轴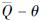 曲线又缓又低,承载力不高但延性好,不容易失效,当轴、轴构件被压垮时,轴、轴构件延性尚未发挥作用便被楼板牵连而倒塌。实际上同一层构件的刚度、延性差异过大,有些构件并未遍历(比如轴、轴)倒塌的3个过程(弹性变形、屈服、倒塌)。这就是“变形饱和”机制的倒塌模式,它区别于因“弱柱强梁”而导致的“层屈服”机制倒塌模式。Paulay等(1992)认为,在层屈服倒塌机制中,同一层的构件共同经历了图 13所示的弹性变形、屈服、倒塌三个过程,这与现实情况是不符的。
曲线又缓又低,承载力不高但延性好,不容易失效,当轴、轴构件被压垮时,轴、轴构件延性尚未发挥作用便被楼板牵连而倒塌。实际上同一层构件的刚度、延性差异过大,有些构件并未遍历(比如轴、轴)倒塌的3个过程(弹性变形、屈服、倒塌)。这就是“变形饱和”机制的倒塌模式,它区别于因“弱柱强梁”而导致的“层屈服”机制倒塌模式。Paulay等(1992)认为,在层屈服倒塌机制中,同一层的构件共同经历了图 13所示的弹性变形、屈服、倒塌三个过程,这与现实情况是不符的。
得妥镇中心小学宿舍楼位于2022年泸定6.8级地震的Ⅸ度区,为4层砌体结构,宿舍楼正面如图 14a所示; 地震后该建筑完好,如图 14c、d所示。现场勘查发现,宿舍楼是内廊对称布局,一层、二层以上建筑平面图如图 15a、b所示,一层3D示意如图 14b所示。
宿舍楼纵向四道轴线,即便纵墙上设有门窗洞口,但开洞率相近,各轴线抗侧刚度相近; 横向七道轴线,布局对称,而且二至四层布置相同(图 15b),质量、刚度竖向连续。整栋建筑布置均匀规整,结构体型规则,抗侧力构件的质量、刚度、强度分布均衡对称,且具有完善的圈梁构造柱抗震措施,符合抗震概念设计原则,不存在上文指出的建筑结构抗震缺陷。
由图 15a可知,在轴、轴上分配的地震剪力是在轴、轴上分配的地震剪力的2倍,各轴分配的地震剪力较均衡,在各轴抗侧刚度相差也不大; 地震作用较小时,各轴剪力较小,结构的变形较小,处于弹性阶段; 地震作用增大后,结构变形尚未达到结构破坏点,未发生明显的破坏,且所受地震剪力小于结构的抗力,从而使结构可以抵御地震作用,如图 15c、d所示。
按照建筑结构变形饱和倒塌机理,该建筑的抗侧和承重构件整体约束情况相同,同层各类构件的抗震性能相近,有效避免了内力集中,没有构件率先达到变形饱和状态,因此,该建筑即使处于极震区,仍然未发生任何震损。这种建筑物抗御超设防水准地震作用,依靠的不是建筑结构关键构件的塑性变形或延性,而是构件间内力的均衡分配。
本文通过总结建筑结构震害特点,分析了地震中发生破坏和倒塌的各类房屋建筑的结构形式、建筑平立面布置、抗侧力构件分布及结构体系,认为结构破坏、倒塌是其自身存在“散”“脆”“偏”“单”等抗震缺陷,其中“偏”的缺陷较其他缺陷更普遍。揭示了建筑结构中“硬脆”构件和“弱延”构件同层并存是破坏和倒塌的主要原因,得出了以下结论:
(1)地震中建筑结构破坏甚至倒塌是由个别构件或局部构件先破坏引起的,建筑结构存在的“散”“脆”“偏”“单” 等抗震缺陷,结构破坏倒塌过程中有可能是其中一个或多个缺陷导致的。
(2)建筑结构中填充墙的布设使结构同层各抗侧承重构件的力学性能截然不同,由硬脆构件和弱延构件同层并存,其中硬脆构件通常是引起结构倒塌的触发点,这与目前传统抗震设计理论将同一层所有构件同等看待,且均等抵御地震作用有着本质的不同。
(3)传统抗震理论强调结构承载力和延性的组合抵御设定的地震作用。变形饱和倒塌机理强调构件间内力分配均衡,只要楼层中各抗侧力构件内力均衡分配,结构就难以破坏,即具有合理约束,避免“偏”的缺陷,结构就具有很好的抗震能力。